
Why Indian Matchmakers Stands Out
March 3, 2025
Red Flags to Watch Out for When Using Online Dating and Matchmaking Sites in India
March 4, 2025
Why Indian Matchmakers Stands Out
March 3, 2025
Red Flags to Watch Out for When Using Online Dating and Matchmaking Sites in India
March 4, 2025Current Trends in Indian Marriages

Marriage in India has always been a deeply rooted cultural institution, evolving significantly from the time of independence in 1947 to the present day. This blog delves into the dynamic journey of marriage in India, highlighting the key changes in societal attitudes, legal frameworks, and demographic trends.
The Early Days: Post-Independence to the 1970s
Right after India gained independence, marriage was predominantly an arranged affair. Families played a crucial role in finding suitable matches for their children, often focusing on factors like caste, community, and economic status. Child marriages, though legally banned by the Child Marriage Restraint Act of 1929, were still common, particularly in rural areas.
Key Characteristics:
- Arranged marriages were the norm.
- Child marriages were still prevalent.
- Limited legal protection for women within marriage.
The Modern Era: 2000s to Present
The 21st century brought rapid changes to Indian society. Urbanization, increased female education, and greater workforce participation significantly impacted traditional marital norms. Love marriages became more common, and there was a growing acceptance of inter-caste and inter-religious unions.
Statistical Insights
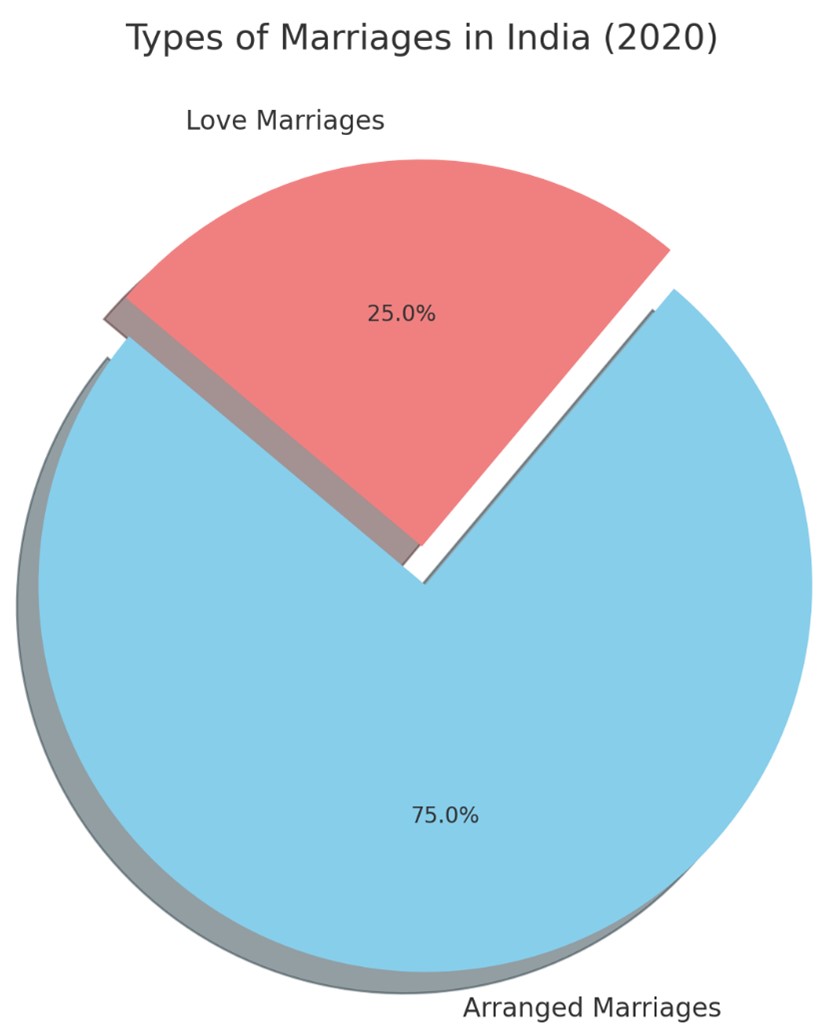
1. Types of Marriages:
While arranged marriages still dominate, they now constitute about 75% of all marriages. Love marriages have increased to 25%.
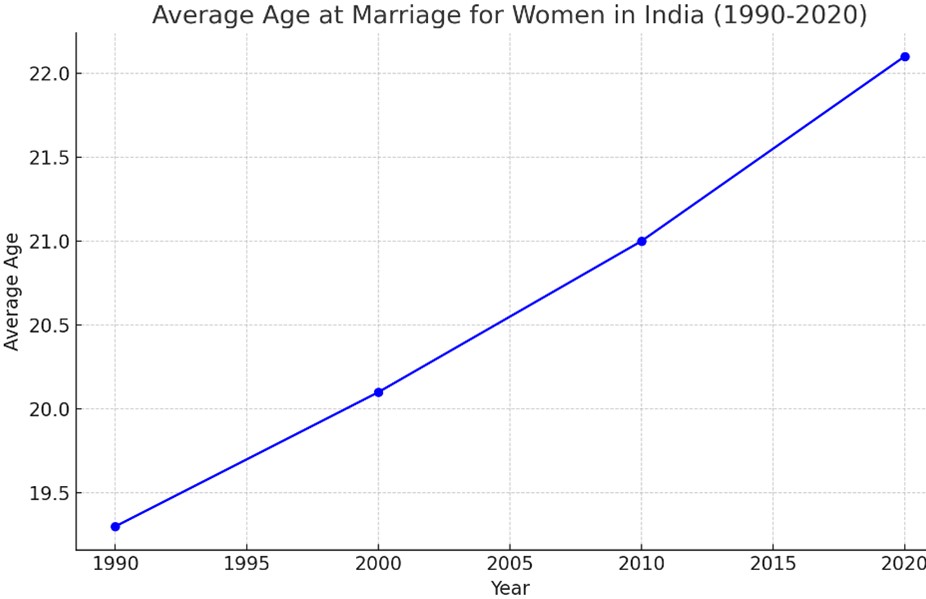
2. Age at Marriage:
The average age at marriage for women rose from 19.3 years in 1990 to 22.1 years in 2020.
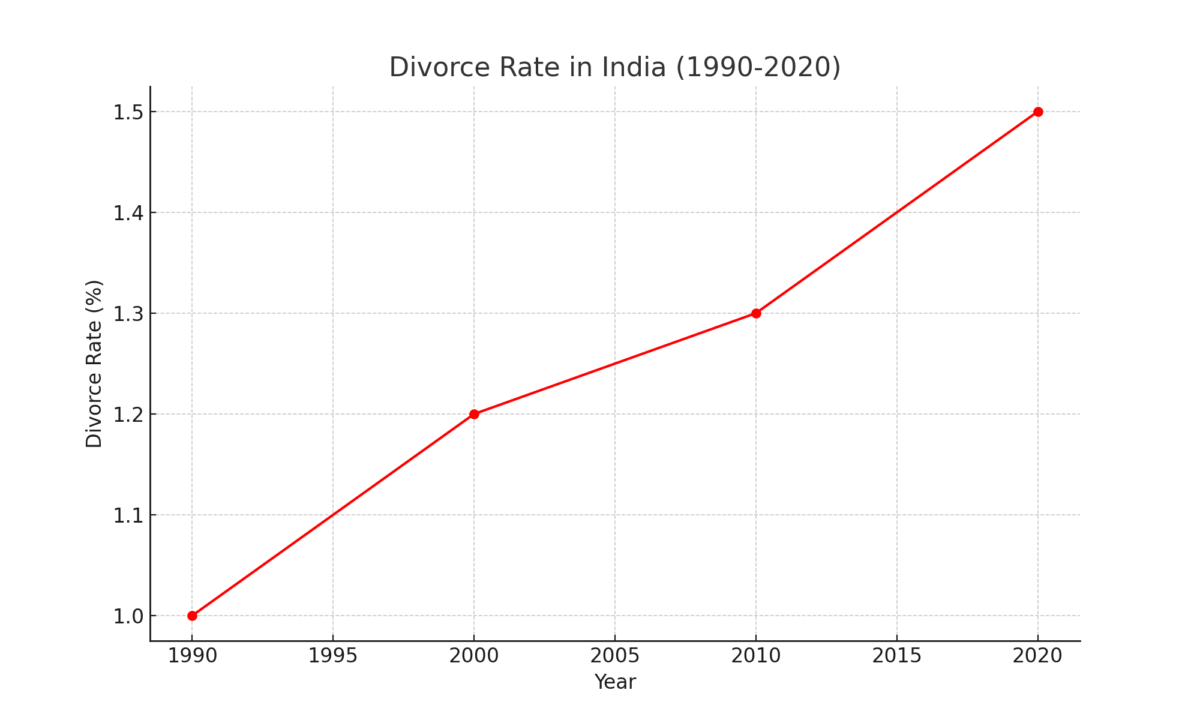
3. Divorce Rates:
The divorce rate, though still low compared to Western countries, increased from 1% in 1990 to 1.5% in 2020.
Changing Trends and Influences
- Inter-caste and Inter-religious Marriages: There’s been a gradual rise in these marriages, especially in urban areas, despite societal resistance.
- Role of Technology: Online matrimonial sites and dating apps have empowered individuals to choose their partners.
- Gender Roles: Increasing gender equality and shifting economic roles have redefined marital dynamics.
Challenges and Future Outlook
The rural-urban divide still exists, with traditional practices persisting more in rural areas. Despite legal provisions, social acceptance of non-traditional marriages remains a challenge. However, as socio-economic development continues, further shifts towards individual choice and equality in marriage are anticipated.
Conclusion
The journey of marriage in India from 1947 to today reflects a complex interplay between tradition and modernity. While arranged marriages still hold sway, the rising trend of love marriages and greater gender equality points towards a more progressive future. Legal reforms and socio-economic changes will continue to shape the landscape of marriage in India, making it a fascinating area of study and observation.
This blog captures the essence of how marriage in India has evolved, providing a snapshot of the changing norms and the road ahead.

